Water Quality and Advocacy
The issues
“The Evenlode waters used to be crystal clear, then, one summer it seemed, they turned to look like oxtail soup. It is still obvious something is very wrong.”
John Pratt – Catchment Champion for the ECP
One of the biggest threats to freshwater comes from an excessive inflow of nutrients, in particular nitrates and phosphates. Nitrates and phosphates occur naturally in the environment, and healthy freshwater ecosystems usually have small amounts of these nutrients which help to sustain aquatic plant life. However, human activity on land can cause unnaturally high levels of nutrients to enter them.
In the Evenlode, the main sources of poor water quality are sewage and agricultural runoff. Our data shows that sewage accounts for 65–80% of total phosphate pollution in the catchment, with the remainder coming from agriculture. Over the last few decades there have been woeful declines in the quality of water in the Evenlode.


Raw and treated sewage
Raw sewage is only allowed to be spilled to the environment during exceptional weather circumstances. However, we get spills in normal rain, due to inadequate environmental permits. During rain events, and as a result of poorly maintained water and sewage infrastructure, too much rain gets into the pipework entering water Sewage Treatment Works (STWs). When this overload happens, treatment works are designed to divert untreated wastewater to storm tanks, and then spill to the environment. These spills are known as storm overflows. You can check when storm overflows are spilling in real time on Thames Water’s event duration monitoring (EDM) map.
The other issue is treated effluent. Many Sewage Treatment Works (STWs) are designed to deal with a ‘usual’ amount of wastewater, during dry weather flows. The problem is that most of the STWs in the Evenlode don’t remove excessive nutrients like phosphorous, nitrates, microplastics and other contaminants. These enter the river from the treated effluent. These nutrients cause a chronic problem for water quality which causes algae, diatom and fungal growth.
Additional treatment is required to better purify wastewater and rid it of excessive nutrients and chemicals.

Agricultural runoff
Historically, high amounts of phosphates and nitrates have washed off agricultural land into the rivers. Thanks to farmers and landowners in the Evenlode, and catchment sensitive farming incentives, the pollution from farming is greatly reduced. However, we want to see increased action and financial incentives to continue this reduction in farming pollution.
The impacts
The poor water quality has had the following effects on aquatic life and river users:
- Fish stocks between 2010 and 2020, particularly coarse fish, have plummeted to 16% of the levels they were in the 1990s.
- Phosphate and nitrate results from citizen science are above recommended environmental limits.
- Riverfly insects (macroinvertebrates) abundance, collected by citizen science, are diminishing below sewage outfalls.
- Plant life like water crowfoot used to be seen extensively in recent decades, it is now seldom seen.
- Families who used to regularly enjoy the river for bathing and wild swimming, are now afraid of their life to get in.
- Kayaking clubs on the Evenlode have abandoned their events due to E- Coli levels in the river.

The significance of water quality
When water quality is good in rivers it brings lots of benefits. This includes, but is not limited to:
- Clean rivers allow ecosystems to thrive.
- Clean water is the most effective public health intervention to prevent disease.
- Clean rivers benefit local business and tourism.
- Clean rivers promote physical and mental well being.
What you can do
Through understanding which areas are being affected by pollution, we can direct targeted mitigation to improve water quality and protect freshwater environments.
If you want to help, there are lots of ways you can get involved, whether that’s as a volunteer citizen scientist, as a funder, or from home.
If you’d like to receive our “News from the Riverbank” newsletter, you can sign up by emailing sfrith@earthwatch.org.uk
Explore some of our projects
Water quality resources
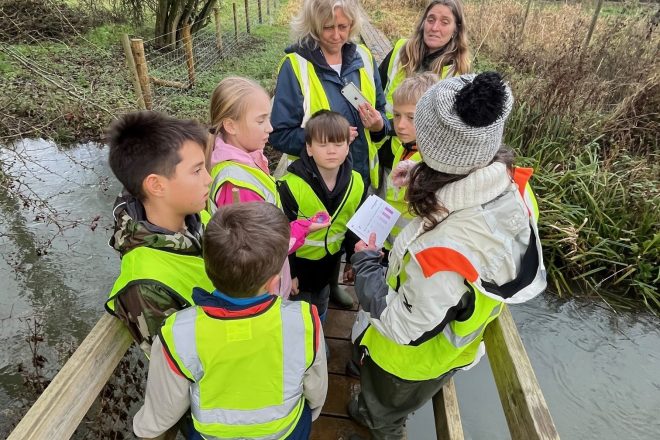

Case Study Leaflet: Citizen Science Schools
Citizen science schools regularly test the water quality of their local rivers and send the data to Earthwatch.
Download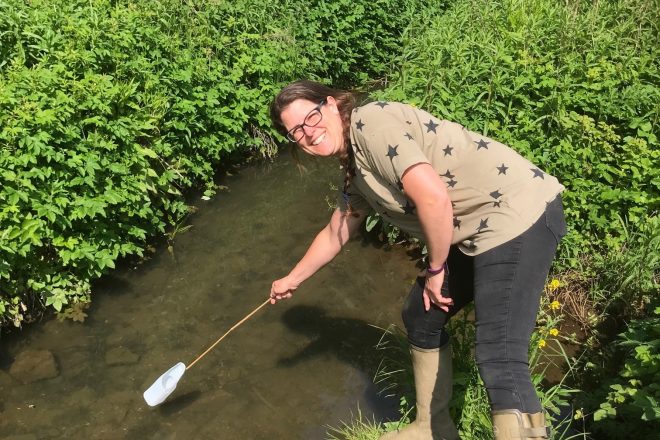
Case Study Leaflet: FreshWater Watch
A citizen science project focusing on monitoring water quality.
Download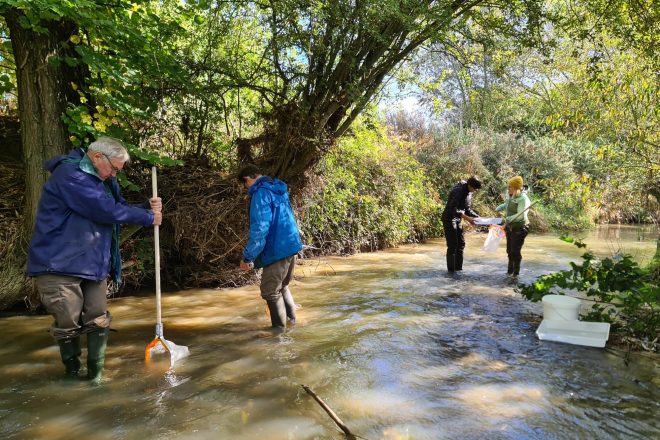
Case Study Leaflet: Riverfly
Surveying riverfly provides an excellent indicator of river health.
Download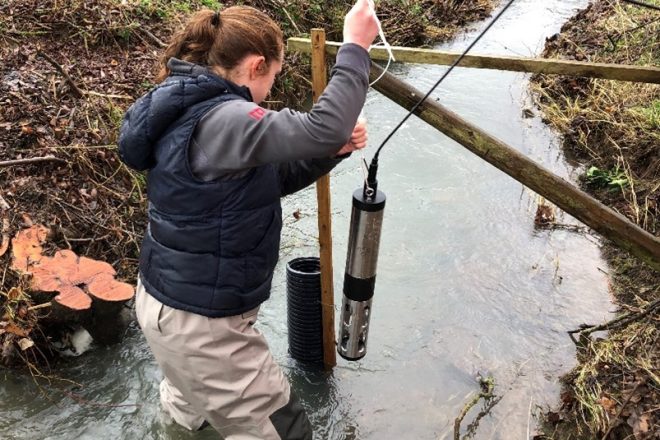
Case Study Leaflet: Sondes
Sondes are real-time near-continuous water quality sensors that provide detailed information and enable investigations into sources of pollution.
Download
Evenlode Annual Water Quality Report 2024
The 2024 annual water quality report for the Evenlode catchment.
Download
Tyre Pollution in the UK’s Rivers: Evenlode Case Study
The frightening chemical soup leaching from our tyres and running off our roads.
Download
ECP Monthly Data Report, December 2024
A synopsis of water quality in the Evenlode catchment for December 2024.
Download
ECP Monthly Data Report, November 2024
A synopsis of water quality in the Evenlode catchment for November 2024.
Download
ECP Monthly Data Report, October 2024
A synopsis of water quality in the Evenlode catchment for October 2024.
Download
ECP Monthly Data Report, September 2024
A synopsis of water quality in the Evenlode catchment for September 2024.
Download
ECP Monthly Data Report, July 2024
A synopsis of water quality in the Evenlode catchment for July 2024.
Download
ECP Monthly Data Report, June 2024
A synopsis of water quality in the Evenlode catchment for June 2024.
Download
ECP Monthly Data Report, May 2024
A synopsis of water quality in the Evenlode catchment for May 2024.
Download
ECP Monthly Data Report, April 2024
A synopsis of water quality in the Evenlode catchment for April 2024.
Download
ECP Water Quality Monitoring Programme 2024-2025
The agreed approach and guidance to water quality monitoring, data analysis and data dissemination.
Download
ECP Monitoring Report for Littlestock Brook
Water quality status and sources of pollution in the Littlestock Brook, September 2024.
Download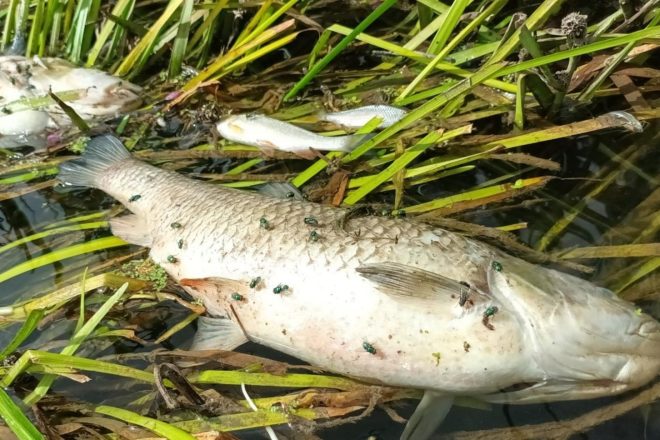
Fish Kill Investigation Guide
A step-by-step guide for citizen scientists to collect vital evidence in fish kill incidents.
Download
Evenlode Annual Water Quality Report 2023
The 2023 annual water quality report for the Evenlode catchment.
Download
How FreshWater Watch data is used
Find out how citizen scientists’ water quality data is used.
Download
ECP Position Statement
A brief prepared by the ECP Water Quality Working Group, October 2021.
Download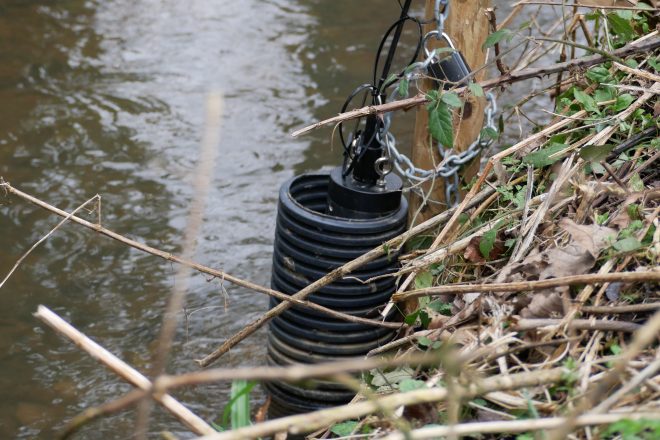
Sondes Data Analysis
An analysis of the October 2024 Sondes data.
DownloadEDM Map
A Thames Water real-time map showing where untreated wastewater has been released.
View Link




